Four Dimensional Model of Virtual Teams
Virtual team is the new reality of 21st century workplace. Large number of HR practitioners as well as organizational leaders has come to acknowledge it as different from traditional teams. They have now shifted their attention towards devising and utilizing new tools and techniques to manage the unique challenges posed by virtual teams.
Jessica Lipnack and Jeffrey Stamps in their book Virtual Teams: People working across Boundaries with Technology (2008) have presented a four-dimensional model of virtual teams.
This model illustrates the four aspects of – purpose, people, link and time, which govern the dynamics of virtual teams. In this article we aim to provide our readers a deep dive into each of these four aspects to ensure a sound understanding of the dimensions of virtual teams as well as to give them a solid thinking platform to reshape their virtual team management strategies.
Figure 1 demonstrates the Four-Dimensional Model of Virtual Teams. This model represents that in virtual teams people are linked through a common purpose over time. The success, failure and challenges of any virtual team precipitate from the interaction among these four dimensions.
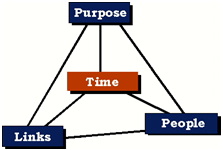
Figure 1: Four Dimensional Model of Virtual Teams
Each of these four dimensions can be further analyzed in the light of three systems of input, processes and results. This produces a total of 12 elements which together define any virtual team. This is illustrated in Figure 2 below.
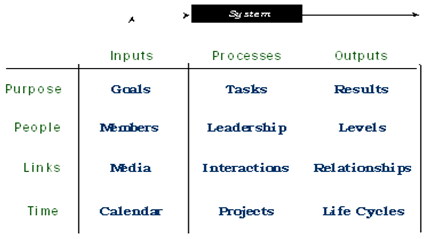
Figure 2: The Elements of Virtual Teams
Now let us look at each of the dimension with its three elements in greater details
Purpose
Purpose acts as binding force for a virtual team. The commitment of the members to a shared common purpose guides them in their day-to-day tasks. A clear purpose transpires into more specific tasks, roles and responsibilities of each member.
Each member has both independent and interdependent sets of tasks. As all the tasks are delivered accurately, the team achieves its final output which is measurable. Clear goals, independent and interdependent tasks, and measurable results guide the team to work towards desired direction.
People
Virtual teams are more than just technology. It is about how members of the virtual team relate to both internal as well as external environment.
Members of a virtual team have to work at two organizational levels - internal which involves working independently and working with other members of the same team; external which involves working in coordination with members of other teams such as vendors, customers etc.
A productive virtual team demands integration at both internal and external levels under the shared leadership.
Links
The virtual team members are linked through the multi-media tools such as emails, videoconferencing and instant messaging etc to continuously interact with each other. Such interactions reduce the boundaries between them, facilitate work processes and aid decision making.
Due to the absence of any physical interactions, the interactions supported by multi-media build workplace relationships; develop trust among the virtual team members and form bonds necessary to perform efficiently and effectively. Trust is a critical success factor for any virtual team.
Time
Virtual team does not give an opportunity to its leaders to call all the team members for a meeting at same place and at same time. It necessitates collaboration of efforts to match each member’s work calendar to schedule meetings and discussions for tracking projects.
For any successful virtual team, it is important to set the ground rules at the formative stage itself. This leaves little room for any confusion and conflicts later during the performance stage. Thus each virtual team has to pass through the stages of a team development lifecycle.
Conclusion
Thus we see how the four dimensional model of virtual teams along with its 12 elements forms the general principles of virtual teams. This theoretical framework when put in practice yields appreciative results. Most of the tools and techniques for managing virtual teams discussed in later articles are derived from this framework.
| ❮❮ Previous | Next ❯❯ |
 Related Articles
Related Articles
- Reasons for Failure of Virtual Teams
- Degree of Virtuality in Teams
- Role of Virtual Team Members
- Competencies of Virtual Team Members
- Success Factors for Virtual Teams
Authorship/Referencing - About the Author(s)

The article is Written and Reviewed by Management Study Guide Content Team. MSG Content Team comprises experienced Faculty Member, Professionals and Subject Matter Experts. We are a ISO 2001:2015 Certified Education Provider. To Know more, click on About Us. The use of this material is free for learning and education purpose. Please reference authorship of content used, including link(s) to ManagementStudyGuide.com and the content page url.